VI Representing
Gravitational Waves data
VI.1 Series
plots
Since the user may want to use the Framelib to access the frames, and since
there are many structures defining time-series that can be used, there is a need
for a class or set of classes defining a representation of a time-series or
spectral series. There are two such classes, VSPlot for 1 dimensional plots and
VSPlot2 for 2D.
The class VSPlot is the graphical representation of a series. For the time
being, VSPlot derives from TH1D (histogram class) and adds some minor
methods.
The drawing of VSPlot produces time series specific information such as the
duration, mean value, etc... written in a statistical box.
As we will see, VSPlots are generally created and managed by graphical
managers called VManagers. A VManager holds a potentially big number of plots
and takes care of their deletion if necessary.
One can refer to examples in macros peak.C and peak2.C.
VI.2 Graphical
managers of frames
VI.2.1 Definition
of managers
The manager classes are the heart of the graphical part of the VEGA
environment. They make the interface between the objects and libraries used by
GW experiments, such as the framelib, frames and vectors, and the ROOT
framework.
VManagerFrameL, is a class describing a manager that uses the Framelib for
all its input/output of frames/vectors. We can have in the future a class named
VManagerFramecpp that will use the frame class library Framecpp instead. It is
not important to understand what VManagerFrameL exactly does, this will be
explained in the next paragraph.
What do we want a general VManager to do ? Basically anything related to
the interface between frames and VEGA. A first tentative list that will soon get
longer may be:
- Drawing of vectors(1D and 2D)/series/images/
- Drawing of distributions of series/data
- Management of the VSPlots produced
- Etc...
VI.2.2 Building
a manager : the global gVM
The first thing to know when one wants to use a manager is how to fire it
up. One starts a manager by building a new object of a VManagerXXX class. For
example to start a manager using the FrameLib, one does :
- vmgr = new VManagerFrameL();
This is valid with the
interpreter. In a program, one should also declare the vmgr
variable as a pointer to a VManagerFrameL.
In VEGA, there is a global variable called gVM that is already declared as
a VManagerFrameL and one can use it as he/she wants. gVM is the current
VManager. If one declares another manager, gVM will point to it.
In practice, you can just forget about building a manager and use the
standard gVM provided
VI.2.3 General
use
Once building is done, which is by default the case when you launch vega,
one has to call methods from the declared gVM object. For example :
- gVM->Draw(frame,"adc.IFO_DMRO");
will draw the
data from the "IFO_DMRO" adc contained in the frame "frame" which is a FrameH
structure loaded with standard Framelib calls. It will take care of creating a
VSPlot or a VSPlot2 depending on the dimension of the vector.
We are going in the next paragraphs to concentrate on the manager that uses
the Framelib. Almost the same routines will be available if another (C++ based)
frame manager software is written and interfaced with VEGA.
VI.2.4 Drawing
methods
VI.2.4.1 Drawing
contents and distribution of frame vectors
Simple drawing of a vector in the form of a VSPlot or VSPlot2 :
- void Draw(FrVect vect, Float_t offset, Float_t dur=1e20, Option_t
*option="");
where
- vect is a frame vector of type FrVect that has been
extracted from a frame.
- offset is the offset from which the drawing starts, with
respect to the starting value of the vector (i.e. series).
- dur is the length of the drawn part of the vector (i.e.
series).
- option is an option string that is passed to the plot that
is drawn. For the time being, this is equivalent to the TH1 class drawing
options. The reader can go to the address http://root.cern.ch/ to see the list
of options in the drawing of a TH1 (see Classes and Members Reference
Guide).
If offset and dur are
omitted, the whole vector is drawn. It is also possible to specify only the
drawing option.
A VSPlot is drawn in the current pad or canvas. The address of this plot is
added to the list of plots managed by this manager. The name of the plot becomes
the name of the FrVect.
Examples :
Suppose a time series vector vect contains data starting at
t=0, and has a duration of 1 s, with 50000 samples.
gVM->Draw(vect) will draw the entire series.
gVM ->Draw(vect,0.3,0.2) will draw the series starting
at t0=0.3 s for a duration of 0.2 s, which represents 10000
samples.
gVM ->Draw(vect,"same") will draw the entire series on
the same plot as a previous draw.
Drawing the distribution (histogram) of the data contained in an
FrVect
void DrawHist(FrVect vect, Float_t offset=-1e20, Float_t
dur=1e20, const Text_t *hwork="", Option_t *option="");
Makes a distribution of the values contained in a series. This method
generates or uses a histogram of the class TH1F. If the histogram is generated,
its limits are determined automatically to be +/- 5% of the max and min value in
the series and this histogram has 100 bins.
The variables are :
- offset is the offset from which the histogramming starts,
with respect to the starting value of the series.
- dur is the length of the histogramed part of the
series.
- hwork is, optionally, the name of an existing histogram, for
example "histo1". This allows using any limits for the histogram, provided the
user defines one before calling DrawHist. The contents of the histogram are
erased before filling by the new values, except if a "+" precedes the name, as
in "+histo1". In this case, the data is appended to the histo. If the name hwork
is given but there is no already existing histogram of that name, a new one is
created with standard characteristics.
- option is an option string that is passed to the drawn
histogram of type TH1F. For the time being, this is equivalent to the TH1 class
drawing options. The reader can go to the address http://root.cern.ch/ to see
the list of options in the drawing of a TH1 (see Classes and Members Reference
Guide).
Examples :
Let's assume that a time series vect contains data starting
at t=0, and has a duration of 1 s, with 50000 samples. The min value is -123,
the max value is 212.
gVM->DrawHist(vect,0.2,0.4)
will draw the histogram of the values in vect beginning at
t0=0.2 s for a duration of 0.4 s. The generated histogram has limits
[-130,223].
h1 = new TH1F("h1","test histo",100,-25,25);
gVM->DrawHist(vect,0.2,0.4,"h1");
will generate the histogram h1, with limits [-25,25].
Calling the DrawHist method will fill this histogram but only with the values in
its range. So one can concentrate on the distribution of values around
0.
gVM->DrawHist(vect,0.2,0.4,"+h1");
This will do the same thing as before but without erasing the values of the
histogram before filling. It will just add those to the existing ones. That way,
one can span more than one series for one given histogram.
VI.2.4.2 Drawing
selected contents or distribution of a frame
One can draw a selected adc or processed or simulated data without having
to extract it first from a frame.
Simple drawing of a vector (1D or 2D) contained in a frame :
- void Draw(FrameH frame, Text_t* typeAndName, Float_t offset, Float_t
dur=1e20, Option_t *option="");
where
- frame is a frame of type FrameH that has been read from a
file.
- offset is the offset from which the drawing starts, with
respect to the starting value of the vector (i.e. series).
- dur is the length of the drawn part of the vector (i.e.
series).
- typeAndName is a pointer to an array of char that describes
the type (adc, proc or sim) and name of the frame element to be extracted and
drawn. It has the following structure : "type.name". For example "adc.IFO_DMRO"
is a good format. It will look for the adc data of the adc named "IFO_DMRO". It
is possible to give only the name, if there is no ambiguity. In that case, adc
data will be searched first for that name, then proc and then sim data. If more
than one identical name was used, the first found series will be extracted.
- option is an option string that is passed to the plot that
is drawn. For the time being, this is equivalent to the TH1 class drawing
options. The reader can go to the address http://root.cern.ch/ to see the list
of options in the drawing of a TH1 (see Classes and Members Reference
Guide).
If offset and dur are
omitted, the whole vector is drawn. It is also possible to specify only the
drawing option.
A VSPlot is drawn in the current pad or canvas. The address of this plot is
added to the list of plots managed by this manager. The name of the plot becomes
the name of the FrXXXData extracted (XXX = Adc, Proc or Sim).
Examples :
Suppose a FrAdcData vector "MYGO_ADC" contains data
starting at t=0, and has a duration of 1 s, with 50000 samples in a frame called
"frame".
gVM->Draw(frame,"adc.MYGO_ADC") will draw the entire
series.
gVM ->Draw(frame,"MYGO_ADC",0.3,0.2) will draw the
series starting at t0=0.3 s for a duration of 0.2 s, which represents
10000 samples. Since no type (adc proc or sim) was given, it will search for the
first data occurring with this name in the frame.
Example of such a plot :
gVM ->Draw(frame,"MYGO_ADC","same") will draw the entire
series on the same plot as a previous draw.
Drawing the distribution (histogram) of the data of a vector contained in a
frame
- void DrawHist(FrameH frame, Text_t* typeAndName, Float_t
offset=-1e20, Float_t dur=1e20, const Text_t *hwork="", Option_t
*option="");
Makes a distribution of the values
contained in a vector of type FrXXXData (XXX = Adc, Proc or Sim) contained in
the frame "frame" and of type and name typeAndName. This method
generates or uses a histogram of the class TH1F. If the histogram is generated,
its limits are determined automatically to be +/- 5% of the max and min value in
the series and this histogram has 100 bins.
The variables are :
- frame is a frame of type FrameH that has been read from a
file.
- typeAndName is a pointer to an array of char that describes
the type (adc, proc or sim) and name of the frame element to be extracted and
drawn. It has the following structure : "type.name". For example "adc.IFO_DMRO"
is a good format. It will look for the adc data of the adc named "IFO_DMRO". It
is possible to give only the name, if there is no ambiguity. In that case, adc
data will be searched first for that name, then proc and then sim data. If more
than one identical name was used, the first found series will be extracted.
- offset is the offset from which the histogramming starts,
with respect to the starting value of the series.
- dur is the length of the histogramed part of the
series.
- hwork is, optionally, the name of an existing histogram, for
example "histo1". This allows using any limits for the histogram, provided the
user defines one before calling DrawHist. The contents of the histogram are
erased before filling by the new values, except if a "+" precedes the name, as
in "+histo1". In this case, the data is appended to the histo. If the name hwork
is given but there is no already existing histogram of that name, a new one is
created with standard characteristics.
- option is an option string that is passed to the drawn
histogram of type TH1F. For the time being, this is equivalent to the TH1 class
drawing options. The reader can go to the address http://root.cern.ch/ to see
the list of options in the drawing of a TH1 (see Classes and Members Reference
Guide).
Examples :
Let's assume that a FrAdcData vector contains data starting at t=0, and has
a duration of 1 s, with 50000 samples. The min value is -123, the max value is
212 in a frame called "frame".
gVM->DrawHist(frame,"adc.MYGO_ADC",0.2,0.4)
will draw the histogram of the values in the adc "MYGO_ADC"
beginning at t0=0.2 s for a duration of 0.4 s. The generated
histogram has limits [-130,223].
Example of such a plot :
h1 = new TH1F("h1","test histo",100,-25,25);
gVM->DrawHist(frame,"MYGO_ADC",0.2,0.4,"h1");
will generate the histogram h1, with limits [-25,25].
Calling the DrawHist method will fill this histogram but only with the values in
its range. So one can concentrate on the distribution of values around 0. Since
no type (adc proc or sim) was given, it will search for the first data occurring
with this name in the frame.
gVM->DrawHist(frame,"MYGO_ADC",0.2,0.4,"+h1");
This will do the same thing as before but without erasing the values of the
histogram before filling. It will just add those to the existing ones. That way,
one can span more than one series for one given histogram.
VI.2.4.3 Drawing
2D vectors (images or time-frequency plots)
Frame vectors may contain bi-dimensional information such as images coming
from cameras or time-frequency plots. There is no special method for drawing
these 2D plots. One uses gVM->Draw() methods as for 1D and these methods take
care of producing the right plot, 1D or 2D depending on the dimension of the
data.
In the case of 2D, the plot produced is of type VSPlot2. The manager
handles a list of these plots, as well as a list of 1D plots.
Example :
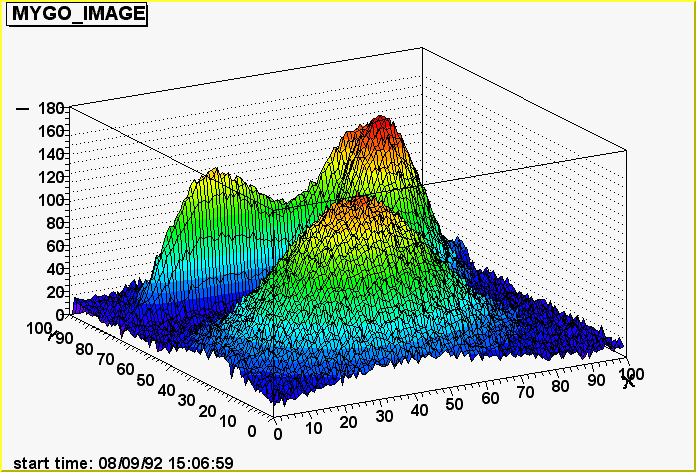
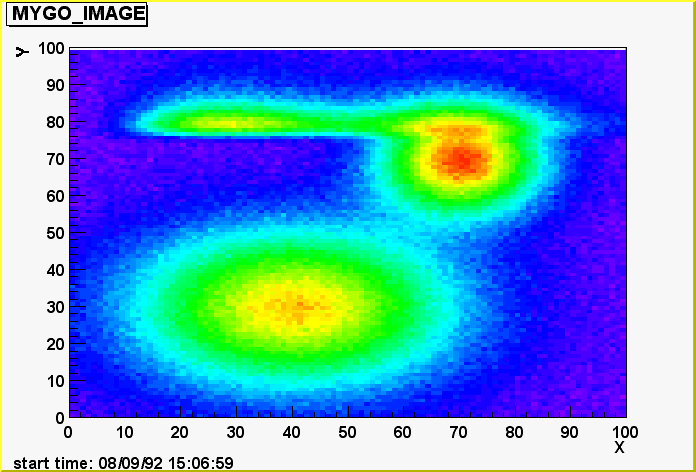
In the files produced by the create_testfr.C script in the vegatutorial
directory, some frames contain images. They are generated as a sum of two
dimensional functions and are there only for demonstration purposes. Once in
vegatutorial, the following lines should show an image:
first, open a database
vega[] vd = new VFrDataBase("demoDB.root")
second, extract the first frame of this database
vega[] fr = vd->GetNextFrame()
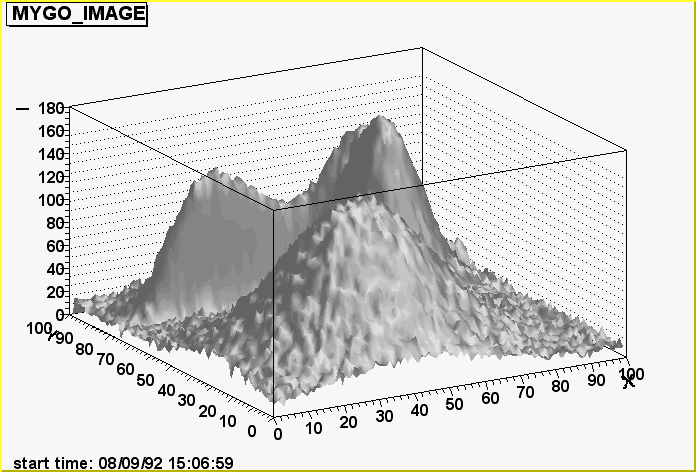
third, since the name of the vector containing the image is "MYGO_IMAGE",
plot it
vega[] gVM->Draw(fr,"MYGO_IMAGE","col")
That's it ! The option "col" used for this drawing produces the third plot
showed hereafter, other options are shown.
|
|
|
|
No option (scatter plot)
|
Option "surf1"
|
|
|
|
|
Option "col"
|
Option "surf4"
|
The options available are the ones of the ROOT TH2 class and are summarized
below:
|
|
- Superimpose on previous picture in the same pad
|
|
|
- Use Cylindrical coordinates
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Use Spherical coordinates
|
|
|
- Use PseudoRapidity/Phi coordinates
|
|
|
- Draw a lego plot with hidden line removal
|
|
|
- Draw a lego plot with hidden surface removal
|
|
|
- Draw a lego plot using colors to show the cell contents
|
|
|
- Draw a surface plot with hidden line removal
|
|
|
- Draw a surface plot with hidden surface removal
|
|
|
- Draw a surface plot using colors to show the cell contents
|
|
|
- same as SURF with in addition a contour view drawn on the top
|
|
|
- Draw a surface using Gouraud shading
|
|
|
- Draw a contour plot (same as CONT0)
|
|
|
- Draw a contour plot using surface colors to distinguish
contours
|
|
|
- Draw a contour plot using line styles to distinguish contours
|
|
|
- Draw a contour plot using the same line style for all
contours
|
|
|
- Draw a contour plot using fill area colors
|
|
|
- Draw a contour plot using surface colors (SURF option at theta =
0)
|
|
|
- Generate a list of TGraph objects for each contour
|
|
|
- Arrow mode. Shows gradient between adjacent cells
|
|
|
- A box is drawn for each cell with surface proportional to
contents
|
|
|
- A box is drawn for each cell, with a color scale varying with
contents
|
|
|
- With LEGO or SURFACE, suppress the Back-Box
|
|
|
- With LEGO or SURFACE, suppress the Front-Box
|
|
|
- Draw plot, but not the axis labels and tick marks (for LEGO and SURF
options)
|
|
|
- Draw a color scale on the right of the plot (for COL and CONT options
only)
|
|
|
- Draw a scatter-plot (default)
|
Since an image is attached to a given frame and does not span two or more
of them, one cannot, for the moment, extract a 2D vector spanning two or more
frames. One could indeed think of it for time-frequency vectors but it is not
yet done.
VI.2.5 Management
of the plots produced
The manager decides at drawing time what is the dimension of the plot
produced depending on the dimension of the data in the frame vector. If the
frame vector is 1 dimensional, it produces a VSPlot, and if it is 2D, it
produces a VSPlot2. The manager then handles two lists of produced plots, one
for 1D and one for 2D.
One can get a pointer to the last created and plotted VSPlot:
- VSPlot* GetLastPlot()
As in :
vega[] VSPlot* vs1 = gVM->GetLastPlot()
This could be useful if one wants to modify this VSPlot, for example to
embellish it. An example is given in the macro "peak2.C".
One can also get a pointer to the last created and plotted VSPlot2
:
- VSPlot* GetLastPlot2()
As in :
vega[] VSPlot2* vs1 = gVM->GetLastPlot2()
This could be useful if one wants to modify this VSPlot2, for example to
embellish it.
VI.3 Representing
slow monitoring data
There are three main powerful drawing methods for slow monitoring data,
i.e. VNtuples. They all enable putting selections, i.e. drawing data that pass
given cuts.
The first method draws VSPlots, which are standard representations of time
series. This method is mainly used to treat slow monitoring data as simple time
series. We encourage you to use this first method since it gives powerful
manipulation (signal analysis) capabilities.
- void DrawSeries(Text_t* varlist, Test_t* cuts, Text_t* option, Int_t
nentries=1000000000, Int_t firstentry=0)
The
parameters are almost identical to the ones of the second method, and are
described below. The only difference is in the "option" parameter.
- option is an option for
drawing:
|
|
- Superimpose on previous picture in the same pad
|
|
|
- Use Cylindrical coordinates
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Use Spherical coordinates
|
|
|
- Use PseudoRapidity/Phi coordinates
|
|
|
- Draw a lego plot with hidden line removal
|
|
|
- Draw a lego plot with hidden surface removal
|
|
|
- Draw a lego plot using colors to show the cell contents
|
|
|
- Draw a surface plot with hidden line removal
|
|
|
- Draw a surface plot with hidden surface removal
|
|
|
- Draw a surface plot using colors to show the cell contents
|
|
|
- same as SURF with in addition a contour view drawn on the top
|
|
|
- Draw a surface using Gouraud shading
|
|
|
- Draw plot, but not the axis labels and tick marks
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Draw a smooth Curve through the plot points
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Draw error bars including bins with o contents
|
|
|
- Draw error bars with perpendicular lines at the edges
|
|
|
- Draw error bars with rectangles
|
|
|
- Draw a fill area through the end points of the vertical error
bars
|
|
|
- Draw a smoothed filled area through the end points of the error
bars
|
|
|
- Draw a line through the plot points
|
|
|
- Draw current marker at each point
|
|
|
- Draw plot with a * at each point
|
The second method draws graphs (sets of points defined by two coordinates).
It will be used in the case of data sets irregularly spaced in time.
- void DrawGraph(Text_t* varlist, Test_t* cuts, Text_t* option, Int_t
nentries=1000000000, Int_t firstentry=0)
- varlist is an expression of the general form e1:e2 where
e1,etc is a formula referencing a combination of the ntuple columns
Example:
varexp = x:y simplest case: draw a plot of points (x,y), x
and y representing columns named x and y
= t:sqrt(x) :
draw plot of sqrt(x) vs t
= log(t):x*y/z
Note that the
variables e1 or e2 may contain a selection.
example, if e1= x*(y<0), the
value plotted will be x if y<0 and will be 0 otherwise.
- cuts is a selection expression. Only ntuple entries passing
this selection will enter into the graph. For example, it could be something
like “t>10 && sin(TP1/6.28) <0”. One can use standard
C operators (+ - * / && || !...) and usual mathematical functions,
including transcendental ones.
- option is an option for drawing. The available options are
:
|
|
- Axis are drawn around the graph
|
|
|
- Time is used for axis labels (not a standard graph feature, added by
VEGA)
|
|
|
- The current marker is drawn at each point
|
|
|
- A simple polyline between all the points is drawn
|
|
|
- A fill area is drawn ('CF' draw a smooth fill area)
|
|
|
|
|
|
- A Star is plotted at each point
|
|
|
- A Bar chart is drawn at each point
|
- Options should be combined to obtain the desired effect. Typically, the
first graph is drawn with option 'AP', to draw the axis, and subsequent plots
that the user wants to overlay are plotted with the 'P' option alone.
- nentries is the maximum number of entries to be processed in
the ntuple
- firstentry is the first entry to be
processed
The second method draws histograms. This is mainly used for statistical
studies.
- void Draw(Text_t* varlist, Test_t* cuts, Text_t* option, Int_t
nentries=1000000000, Int_t firstentry=0)
Unlike in DrawGraph, which needs at least two variables to plot a graph,
one can plot a 1D, 2D or 3D histogram. The variables have the same meaning as in
DrawGraph() but the varlist can contain the name of an existing histo and
options are not the same :
- varlist is an expression of the general form e1:e2 where
e1,etc is a formula referencing a combination of the ntuple columns
Example:
varexp = x:y simplest case: draw a plot of points (x,y), x
and y representing columns named x and y
= t:sqrt(x) :
draw plot of sqrt(x) vs t
= log(t):x*y/z
Note that the
variables e1 or e2 may contain a selection.
example, if e1= x*(y<0), the
value plotted will be x if y<0 and will be 0 otherwise.
One can save the
result of Draw to a histogram:
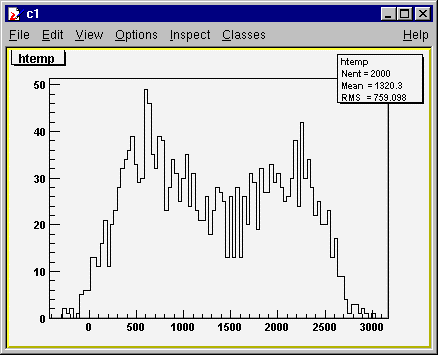
===================================
By
default the temporary histogram created is called htemp.
If varlist
contains >>hnew (following the variable(s) name(s), the new histogram
created is called hnew and it is kept in the current directory (See the class
TDirectory of ROOT).
Example:
vnt->Draw("sqrt(x)>>hsqrt","y>0")
will draw
sqrt(x) and save the histogram as "hsqrt" in the current directory.
By
default, the specified histogram is reset. To continue to append data to an
existing histogram, use "+" in front of the histogram name;
vnt->Draw("sqrt(x)>>+hsqrt","y>0")
will not reset
hsqrt, but will continue filling.
- option is an option for drawing
The following options are
supported on all types:
|
|
- Superimpose on previous picture in the same pad
|
|
|
- Use Cylindrical coordinates
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Use Spherical coordinates
|
|
|
- Use PseudoRapidity/Phi coordinates
|
|
|
- Draw a lego plot with hidden line removal
|
|
|
- Draw a lego plot with hidden surface removal
|
|
|
- Draw a lego plot using colors to show the cell contents
|
|
|
- Draw a surface plot with hidden line removal
|
|
|
- Draw a surface plot with hidden surface removal
|
|
|
- Draw a surface plot using colors to show the cell contents
|
|
|
- same as SURF with in addition a contour view drawn on the top
|
|
|
- Draw a surface using Gouraud shading
|
The following options are supported for 1-D
types:
|
|
- Draw histogram, but not the axis labels and tick marks
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Draw a smooth Curve through the histogram bins
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Draw error bars including bins with o contents
|
|
|
- Draw error bars with perpendicular lines at the edges
|
|
|
- Draw error bars with rectangles
|
|
|
- Draw a fill area through the end points of the vertical error
bars
|
|
|
- Draw a smoothed filled area through the end points of the error
bars
|
|
|
- Draw a line through the bin contents
|
|
|
- Draw current marker at each bin
|
|
|
- Draw histogram with a * at each bin
|
The following options are supported for 2-D
types:
|
|
- arrow mode. Shows gradient between adjacent cells
|
|
|
- a box is drawn for each cell with surface proportional to
contents
|
|
|
- a box is drawn for each cell with a color scale varying with
contents
|
|
|
- same as "COL". In addition the color mapping is also drawn
|
|
|
- Draw a contour plot (same as CONT3)
|
|
|
- Draw a contour plot using colors to distinguish contours
|
|
|
- Draw a contour plot using line styles to distinguish contours
|
|
|
- Draw a contour plot using the same line style for all
contours
|
|
|
- Draw a contour plot using fill area colors
|
|
|
- With LEGO or SURFACE, suppress the Front-Box
|
|
|
- With LEGO or SURFACE, suppress the Back-Box
|
|
|
- Draw a scatter-plot (default)
|
Damir BUSKULIC
Last update :19/11/2001;